Introduction To Assembly Language
Every Computer has a processor, that processor as we have already guessed by its name, processes the information given to the computer. It performs basic operations like arithmetic calculations, logical and control operations for the computer. This processor understands 1s and 0s but for us humans to write code in 1s and 0s is very difficult and tedious so for this purpose assembly language was introduced. Assembly language makes it easy for us to communicate with computer and understand it more clearly.
Assembly language is often called symbolic machine code. It consists of a lot of short forms which is converted to machine language(1s and 0s) when passed through assembler. The following image was found online on the net, it will help you all to understand this concept more clearly.
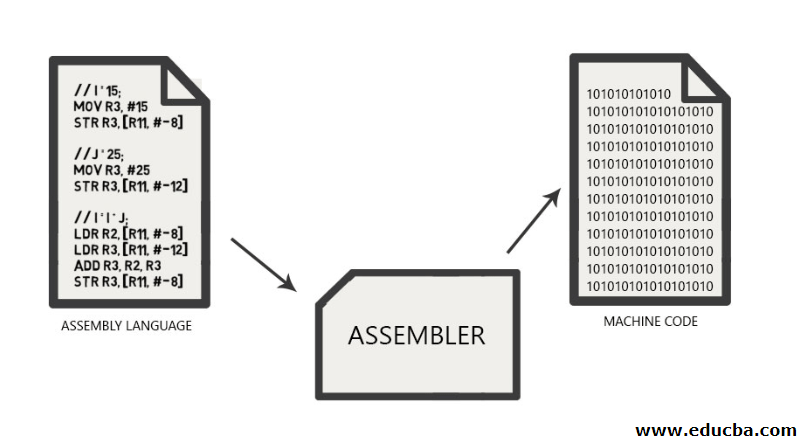
The above process of converting assembly language to machine code is called as assembly.
Ok, so up till now I think I have made my point clear that main purpose of assembly language or should I say every programming language is to understand computer and give it commands.
Now a assembly language is designed depending upon which processor we are using so in short it is processor specific. So it is possible that processor found in one PC may able to assemble code written in it but processor of other PC may not.
Assembly language is a low level language and is often abbreviated as asm. So first of all what is a low level language ?
Low level language does not mean that it is easy to learn or anything. Basically low level language basically means that it is a language that it is very similar to actual machine language and has less abstraction. By abstraction I mean changes added to that language so it becomes less complex and more understandable. The converse of it can be applied for high level languages like python, C, Java etc.
So What exactly are these 1’s and 0’s ?
These 1s and 0s are called bits. It is the smallest possible storage unit of computer.
Bytes
So we have understood bits but what are bytes ? Are they the same thing or different. Well many people think that bits and bytes are same but its false.
Nowadays processor interpret a specific number of bits at a time. They interpret 8 bits at a time. This cluster of 8 bits is known as a byte. The main memory of the computer is composed of an array of bytes, with each byte having a separate memory address. The first byte address is 0 and the last address depends on the hardware and software in use. Any byte that is identified as a machine instruction is pushed into rbp register onto the run-time stack.
After this you all must study the following concepts as it will make your concepts more clear:
- Binary numbers
- Binary arithmetic - addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
- Hexadecimal numbers
- Floating point numbers
I learned the above topics from this book :
Introduction to 64 Bit Intel Assembly Language Programming for Linux